What Is Solar Energy? Every day, the sun radiates (sends out) an enormous amount of energy—called solar energy. It radiates more energy in one day than the world uses in one year. This energy comes from within the sun itself. Like most stars, the sun is a big gas ball made up mostly of hydrogen and helium gas. The sun makes energy in its inner core in a process called nuclear fusion.
What Is Solar Energy?
It takes the sun’s energy just a little over eight minutes to travel the 93 million miles to Earth. Solar energy travels at the speed of light, or 186,000 miles per second, or 3.0 x 108 meters per second. Only a small part of the visible radiant energy (light) that the sun emits into space ever reaches the Earth, but that is more than enough to supply all our energy needs.
Every hour enough solar energy reaches the Earth to supply our nation’s energy needs for a year! Solar energy is considered a renewable energy source due to the fact.
Today, people use solar energy to heat buildings and water and to generate electricity. Solar energy accounts for a very small percentage of U.S. energy—less than one percent. Solar energy is mostly used by residences and to generate electricity.

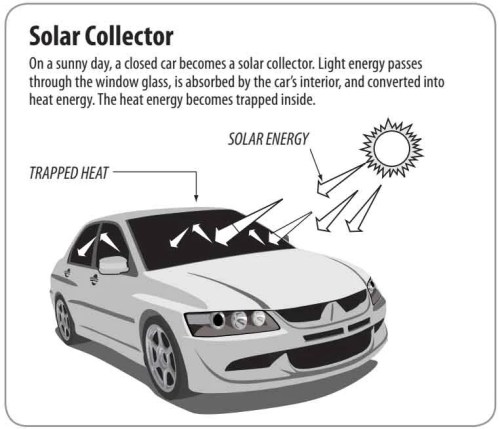
Solar Collectors
Heating with solar energy is not as easy as you might think. Capturing sunlight and putting it to work is difficult because the solar energy that reaches the Earth is spread out over a large area. The sun does
not deliver that much energy to any one place at any one time. The amount of solar energy an area receives depends on the time of day, the season of the year, the cloudiness of the sky, and how close
you are to the Earth’s Equator.
A solar collector is one way to capture sunlight and change it into usable heat energy. A closed car on a sunny day is like a solar collector. As sunlight passes through the car’s windows, it is absorbed by the
seat covers, walls, and floor of the car. The absorbed light changes into heat. The car’s windows let light in, but they don’t let all the heat out. A closed car can get very hot!
Solar Space Heating
Space heating means heating the space inside a building. Today, many homes use solar energy for space heating. A passive solar home is designed to let in as much sunlight as possible. It is like a big solar collector.
Sunlight passes through the windows and heats the walls and floor inside the house. The light can get in, but the heat is trapped inside. A passive solar home does not depend on mechanical equipment, such as pumps and blowers, to heat the house, whereas active solar homes do.

Solar Water Heating
Solar energy can be used to heat water. Heating water for bathing, dishwashing, and clothes washing is the second-largest home energy cost. Installing a solar water heater can reduce your water heating bill by as much as 50 percent.
A solar water heater works a lot like solar space heating. In our hemisphere, a solar collector is mounted on the south side of a roof where it can capture sunlight. The sunlight heats water in a tank. The hot water is piped to faucets throughout a house, just as it would be with an ordinary water heater.

Solar Electricity
Solar energy can also be used to produce electricity. Two ways to make electricity from solar energy are photovoltaics and solar thermal systems.
A. Photovoltaic Electricity
Photovoltaic comes from the words photo, meaning light, and volt, a measurement of electricity. Sometimes photovoltaic cells are called PV cells or solar cells for short. You are probably familiar with
photovoltaic cells. Solar-powered toys, calculators, and roadside telephone call boxes all use solar cells to convert sunlight into electricity.
Solar cells are made up of silicon, the same substance that makes up sand. Silicon is the second most common substance on Earth. Solar cells can supply energy to anything that is powered by batteries or
electric power.
Electricity is produced when radiant energy from the sun strikes the solar cell, causing the electrons to move around. The action of the electrons starts an electric current. The conversion of sunlight into
electricity takes place silently and instantly. There are no mechanical parts to wear out.
Compared to other ways of making electricity, photovoltaic systems are expensive and many panels are needed to equal the electricity generated at other types of plants.
It can cost 10 to 30 cents per kilowatt-hour to produce electricity from solar cells. Most people pay their electric companies about 12.6 cents per kilowatt-hour for the electricity they use, and large industrial consumers pay less. Solar systems are often used to generate electricity in remote areas that are a long way from electric power lines.
In 2015, the Desert Sunlight solar project in California opened. It is among the largest photovoltaic plants in the world, generating 550 megawatts of electricity—enough to power over 150,000 homes.

B. Solar Thermal Electricity
Like solar cells, solar thermal systems also called concentrated solar power (CSP), use solar energy to produce electricity, but in a different way. Most solar thermal systems use a solar collector with a mirrored surface to focus sunlight onto a receiver that heats a liquid. The super-heated liquid is used to make steam to produce electricity in the same way that coal plants do. There are CSP plants in California, Arizona, Nevada, Florida, Colorado, and Hawaii. Some of the world’s largest CSP facilities are located in California.
Solar energy has great potential for the future. Solar energy is free, and its supplies are unlimited. It does not pollute or otherwise damage the environment. It cannot be controlled by anyone nation or industry. If we can improve the technology to harness the sun’s enormous power, we may never face energy shortages again.


















